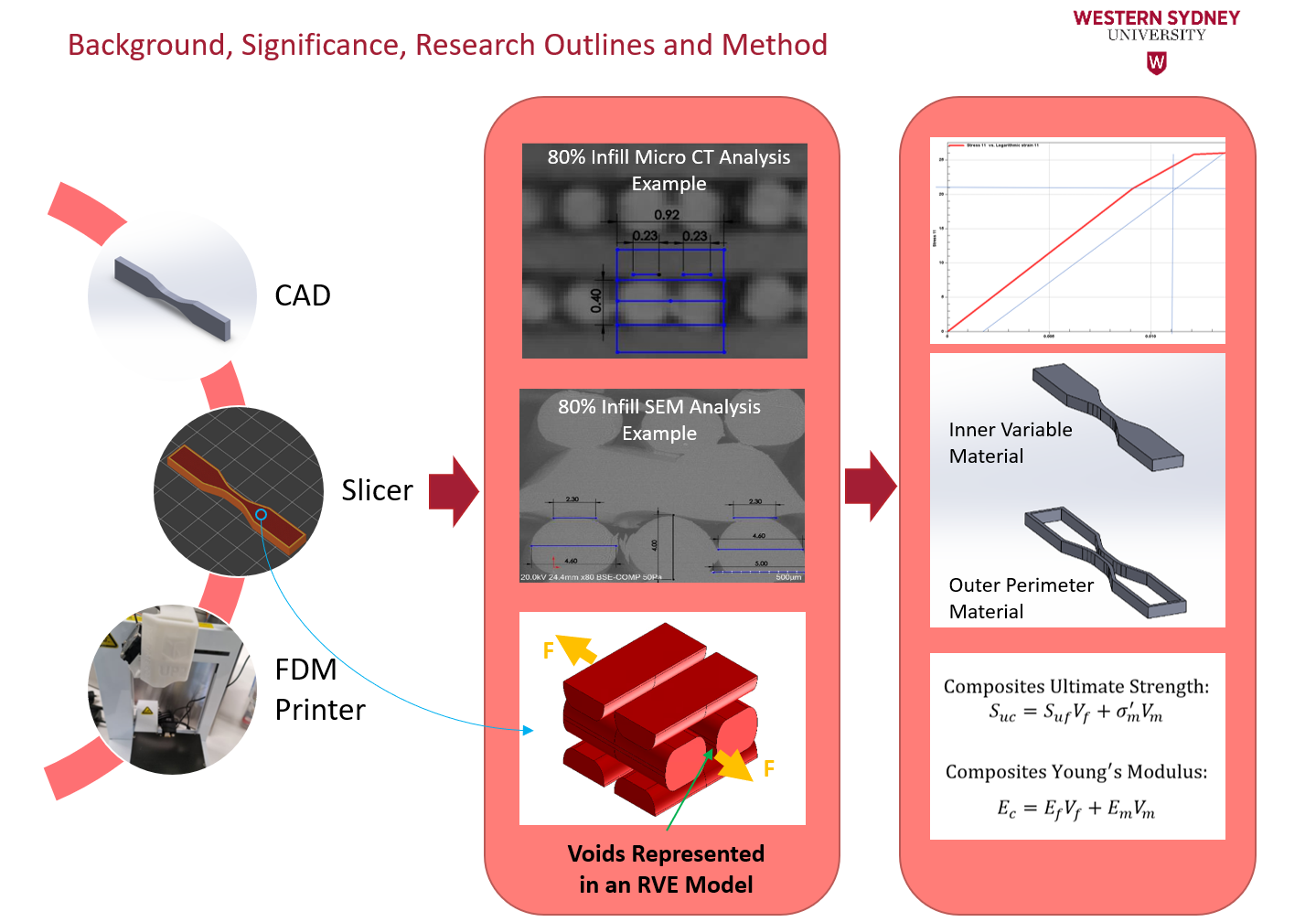
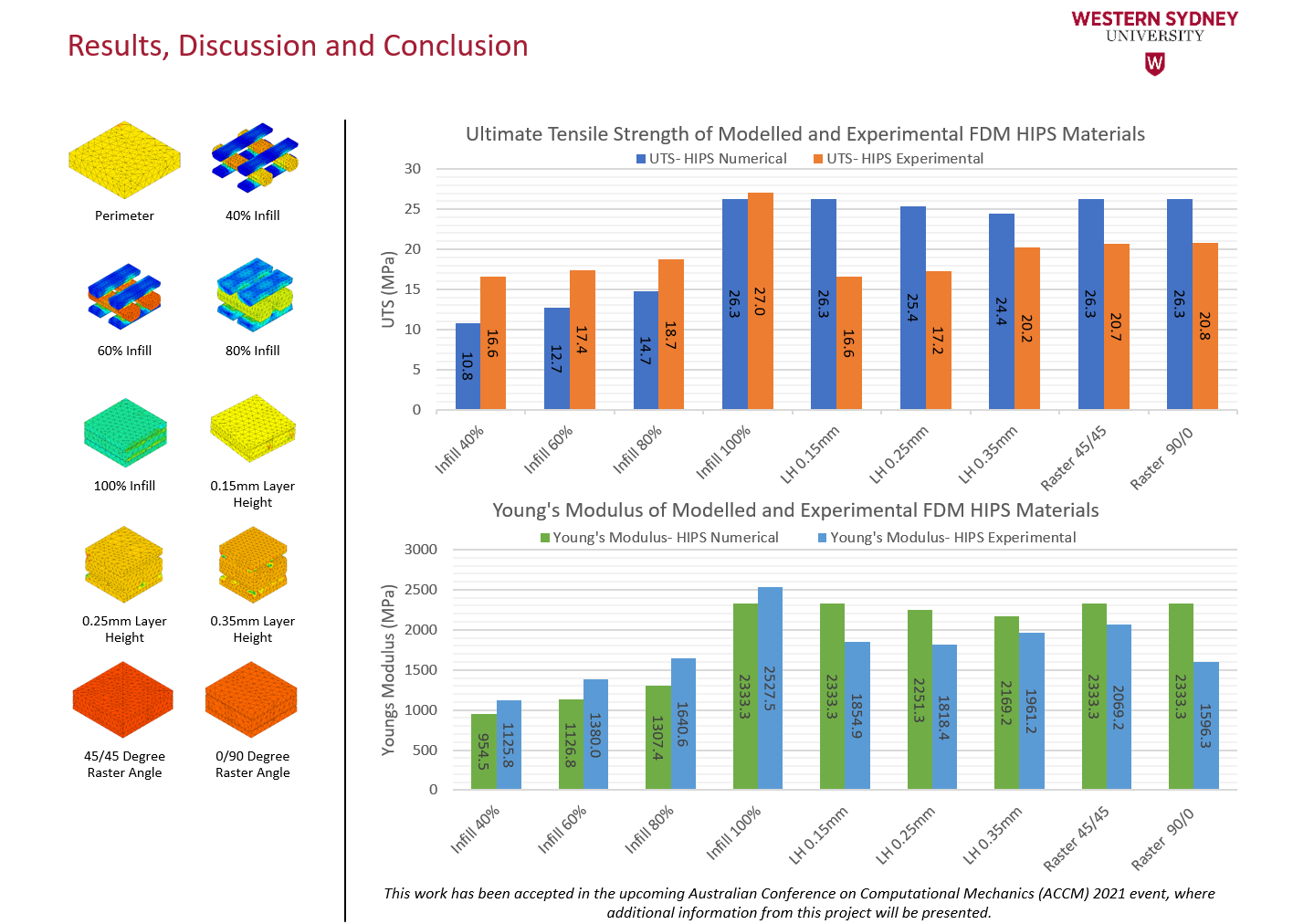
Additively manufactured (AMed) polymer-based materials can provide additional benefits to numerous products, consequent of advantages it has over traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. Although, there are currently drawbacks associated with additive manufacturing that limit its ability to be fully utilised for manufacturing components. One of these drawbacks is the anisotropic properties of AMed materials due to voids, inconsistent layer adhesion and surface defects.
This project aims to develop a multiscale modelling and analysis framework and then utilise it to investigate this issue by accurately modelling AMed high impact polystyrene (HIPS) materials with different printing parameters of a fused deposition modelling (FDM) printer. This will study how their anisotropic properties influence their material properties to provide useful guidelines for high-quality printed products.