Esmaeel Eftekharian
I am currently a senior research associate in the School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. I completed my PhD in Infrastructure Engineering at Western Sydney University, Australia.
My research interest includes wind and fire engineering, bushfire research, Computational Fluid Dynamics, heat transfer, and aeroacoustics.
Variation in wind velocity through fire-wind interaction can potentially damage buildings during bushfires. Fire-wind enhancement which is referred to as the increase of wind velocity during fire-wind interaction is one of the destructive phenomena in this regard. Despite the significance, the underlying mechanism contributing to the phenomena is still not well understood.
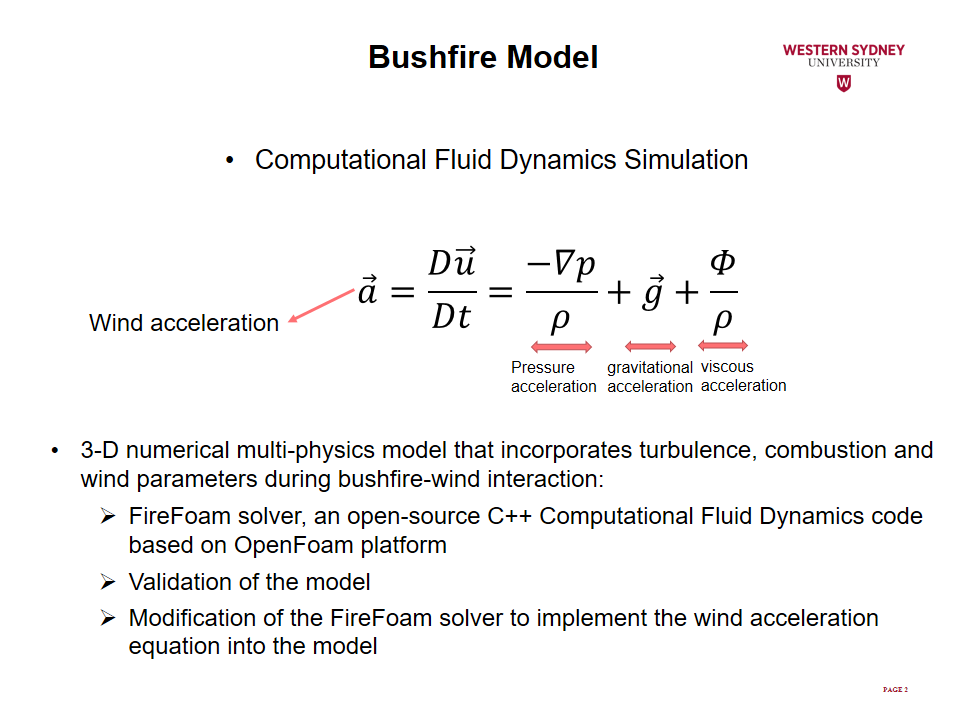
A novel theory based on flow acceleration analysis and the associated fundamental principles of fluid mechanics was developed to explain why wind velocity increases during fire-wind interaction. Based on the developed theory, the factors contributing to the phenomena, including wind velocity, fire intensity, fire source configuration, and terrain slope were studied. Correlations were also developed to predict the extent to which wind is enhanced during interaction with fire.
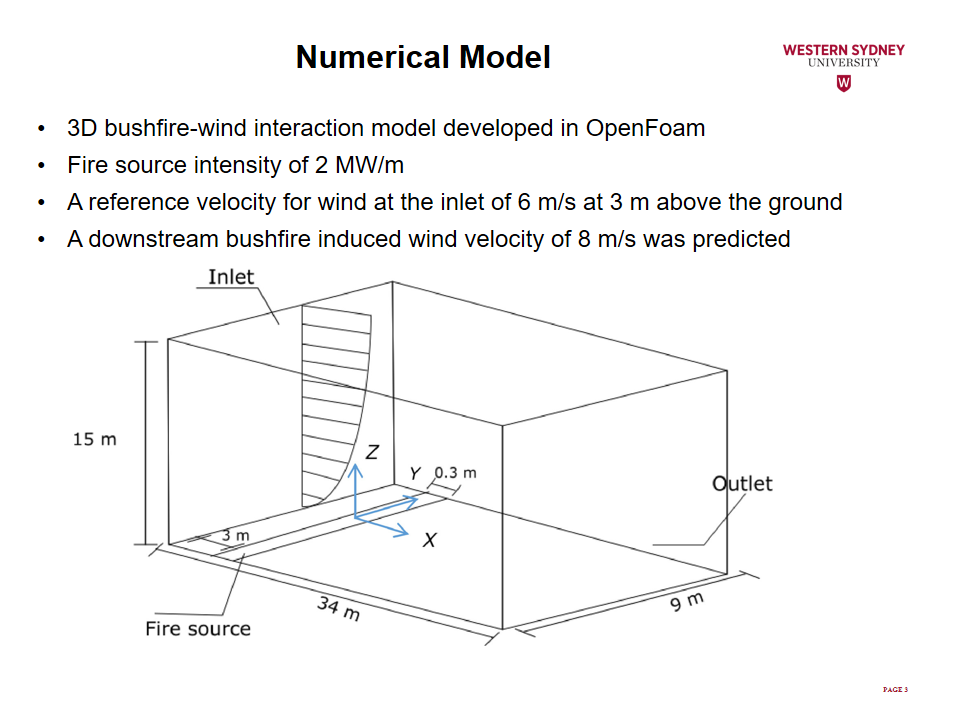
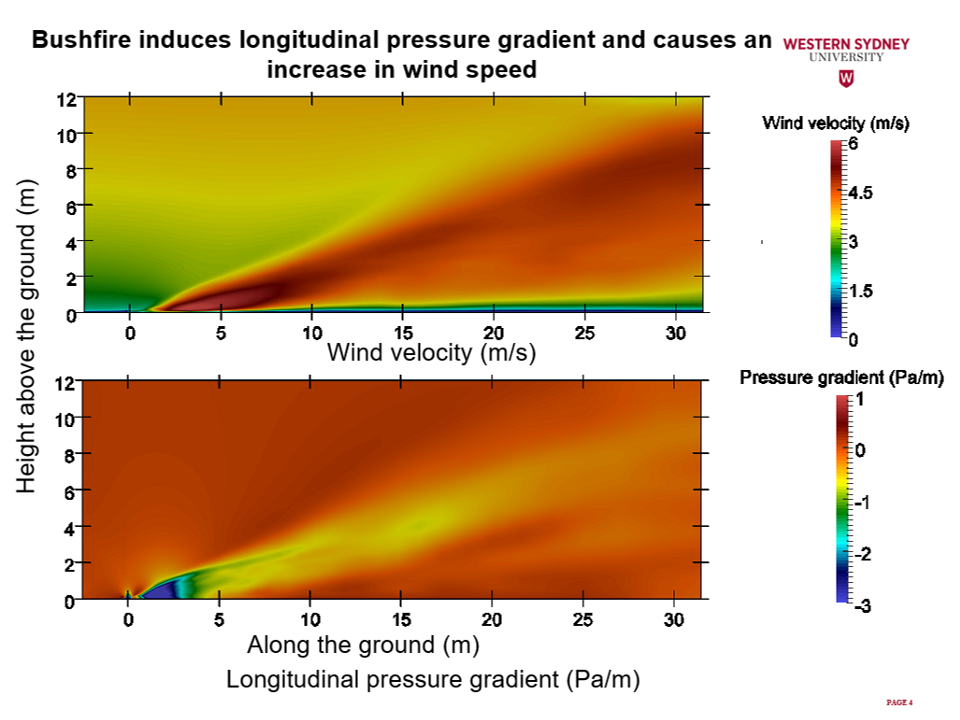
This study uses FireFOAM solver of OpenFOAM platform to perform Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) simulations for fire-wind interaction scenarios. FireFOAM solver was modified to incorporate the developed acceleration theory in order to quantitatively analyse wind enhancement as well as factors contributing to the phenomena. The results revealed that due to the interaction of fire with wind, a fire-induced pressure gradient is generated along the wind direction, accelerating the flow, and causing wind enhancement.